HTML Applications
Build apps with HTML, CSS, and Lua
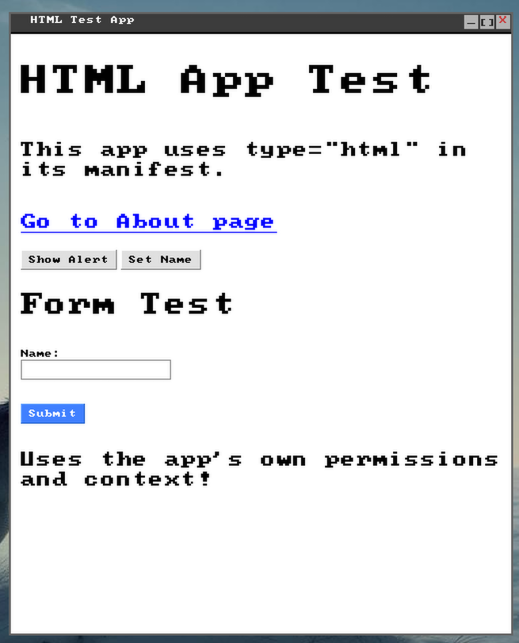
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>HTML Test Application</title>
<meta name="window-width" value="500">
<meta name="window-height" value="600">
</head>
<body>
<h1>HTML App Test</h1>
<p>This app uses type="html" in its manifest.</p>
<p><a href="about.html">Go to About page</a></p>
<button onclick="alert('Hello from HTML app!')">Show Alert</button>
<button onclick="setName()">Set Name</button>
<h2>Form Test</h2>
<form>
<label>Name:</label>
<input type="text" id="name" name="name">
<br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
<script>
console.log("HTML Test App loaded!")
function setName()
query("#name").value = "Test User"
end
</script>
</body>
</html>How It Works
LuajitOS includes a built-in HTML renderer that lets you build graphical applications using familiar web technologies. Unlike Electron, there's no embedded browser - the HTML is rendered directly by the OS.
Key Features
Creating an HTML App
Set type = "html" in your manifest and point entry to your HTML file:
return {
name = "myapp",
pretty = "My HTML App",
type = "html",
entry = "index.html",
permissions = {"filesystem"}
}Lua in Scripts
Inside <script> tags, write Lua code directly. Functions are defined using Lua syntax:
<script>
-- This is Lua, not JavaScript!
function handleClick()
local name = query("#name").value
alert("Hello, " .. name .. "!")
end
-- Access the filesystem
function saveData()
fs.write("/home/data.txt", "Saved!")
end
</script>Window Size
Set the window dimensions using meta tags in your HTML. These override any values in the manifest:
<meta name="window-width" value="500">
<meta name="window-height" value="600">Available APIs
HTML apps have access to the same sandboxed APIs as regular Lua apps, based on their manifest permissions: